Boiler Blog | Nationwide Boiler Inc.
Safety Valves: What, Why, and How
What
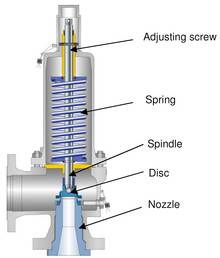
The safety valve is one of the most important safety devices in a steam system. Safety valves provide a measure of security for plant operators and equipment from over pressure conditions. The main function of a safety valve is to relieve pressure. It is located on the boiler steam drum, and will automatically open when the pressure of the inlet side of the valve increases past the preset pressure. All boilers are required by ASME code to have at least one safety valve, dependent upon the maximum flow capacity (MFC) of the boiler. The total capacity of the safety valve at the set point must exceed the steam control valve’s MFC if the steam valve were to fail to open. In most cases, two safety valves per boiler are required, and a third may be needed if they do not exceed the MFC.
There are three main parts to the safety valve: nozzle, disc, and spring. Pressurized steam enters the valve through the nozzle and is then threaded to the boiler. The disc is the lid to the nozzle, which opens or closes depending on the pressure coming from the boiler. The spring is the pressure controller.
As a boiler starts to over pressure, the nozzle will start to receive a higher pressure coming from the inlet side of the valve, and will start to sound like it is simmering. When the pressure becomes higher than the predetermined pressure of the spring, the disc will start to lift and release the steam, creating a “pop” sound. After it has released and the steam and pressure drops below the set pressure of the valve, the spring will close the disc. Once the safety valve has popped, it is important to check the valve to make sure it is not damaged and is working properly.
Why
A safety valve is usually referred to as the last line of safety defense. Without safety valves, the boiler can exceed it’s maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP) and not only damage equipment, but also injure or kill plant operators that are close by. Many variables can cause a safety valve on a boiler to lift, such as a compressed air or electrical power failure to control instrumentation, or an imbalance of feedwater rate caused by an inadvertently shut or open isolation valve.
Once a safety valve has lifted, it is important to do a complete boiler inspection and confirm that there are no other boiler servicing issues. A safety valve should only do its job once; safety valves should not lift continuously. Lastly, it is important to have the safety valves fully repaired, cleaned and recertified with a National Board valve repair (VR) stamp as required by local code or jurisdiction. Safety valves are a critical component in a steam system, and must be maintained.


