In the boiler industry, there are three main types of watertube boilers: D-type, O-type, and A-type (see the graphic). Boilers can be designed for either saturated or superheated steam, and they can be packaged or field-erected. Package watertube boilers are designed to be small enough for highway transportation and are factory assembled. Field-erected boilers are just as they sound; multiple components are assembled and installed in the field.
For each boiler type, there are differences in superheater design and performance. Before diving into those differences, let’s review each of the main types of watertube boilers. 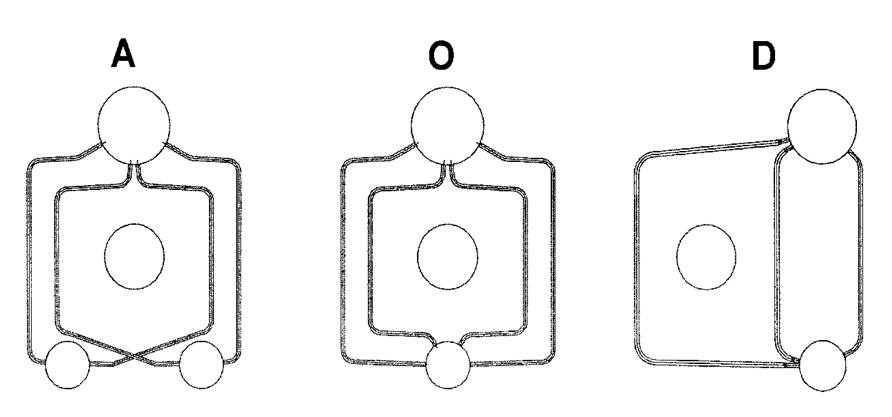
D-type boilers have one steam drum and one lower drum, centered over each other with the furnace offset to one side. These boilers are designed with only one generating bank.
O-type boilers also have one steam drum and one lower drum, however, they are centered over each other with the furnace in the center. These boilers are designed with two generating banks (i.e. the flue gas flow splits into the two sides at the end of the furnace).
A-type boilers are similar to O-type and include two generating banks. The major difference is the number of drums and placement. A-type boilers include one steam drum at the top center, and two lower drums; one placed on each side of the furnace.
Saturated steam means that the steam temperature is purely dependent on the steam pressure and follows the pressure-temperature curve. For example, if the upper drum is at 150 psig, the saturated temperature would be 366°F. If the upper drum is at 300 psig, the saturated temperature would be 422°F. Saturated steam boilers will have a steam nozzle directly on the upper drum regardless of the boiler type. All of the steam produced is also collected in the upper drum.
When the design calls for superheated steam, which would be higher than the saturation temperature, an extra set of steam tubes or coils are provided and added to the heat transfer circuit in the boiler. The superheater tube bank is piped downstream of the steam drum to add heat to the saturated steam and make it superheated.
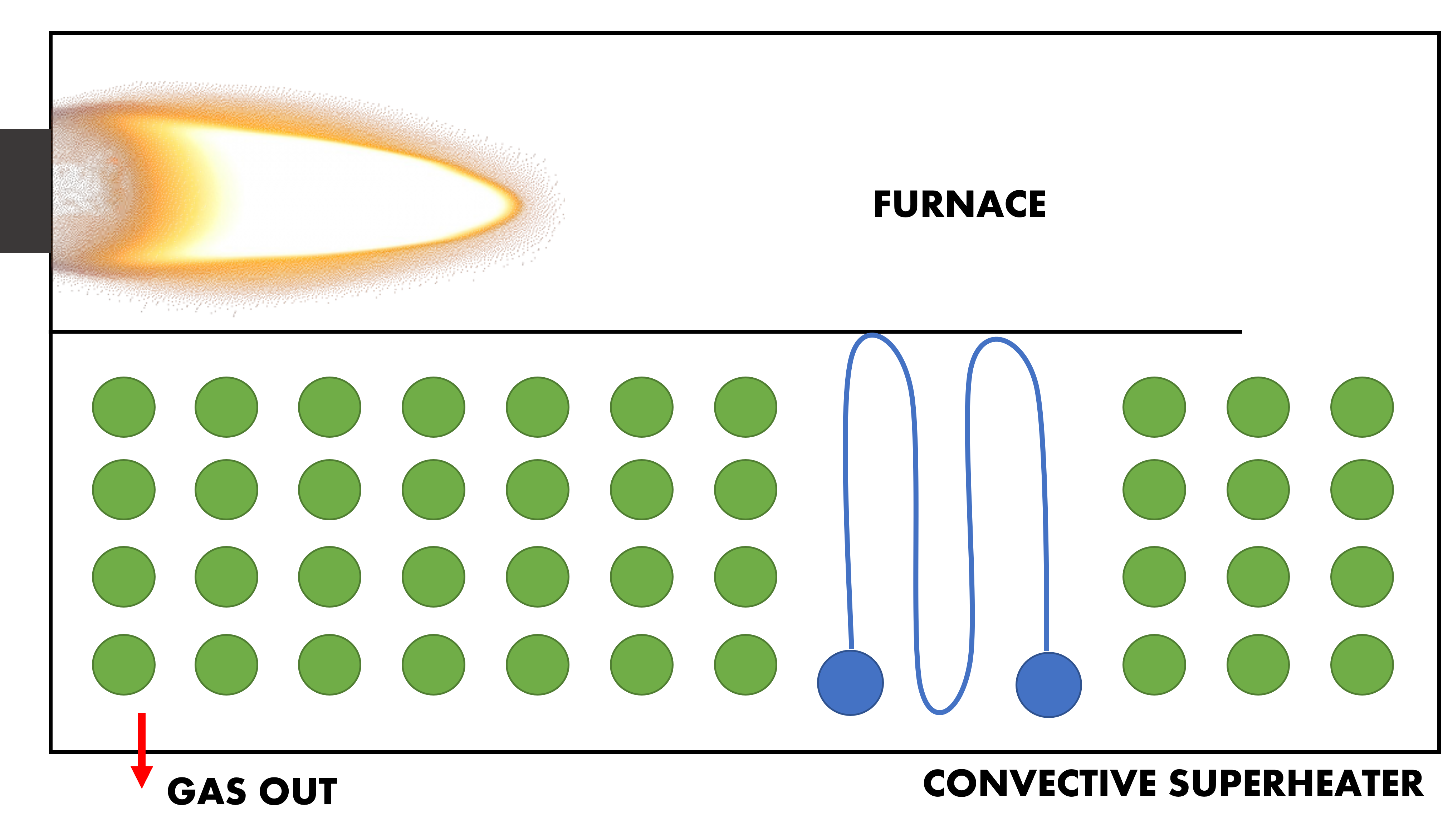 On D-Type boilers, this extra tube bank is added to the convection section (or the generating bank). This is called the convective design. The benefit of this design is the steam coils are out of the radiant heat zone of the burner (the extra heat transferred uses convection only). However, performance is not as good as radiant style superheaters which means at reduced loads, the steam temperature drops off quickly.
On D-Type boilers, this extra tube bank is added to the convection section (or the generating bank). This is called the convective design. The benefit of this design is the steam coils are out of the radiant heat zone of the burner (the extra heat transferred uses convection only). However, performance is not as good as radiant style superheaters which means at reduced loads, the steam temperature drops off quickly.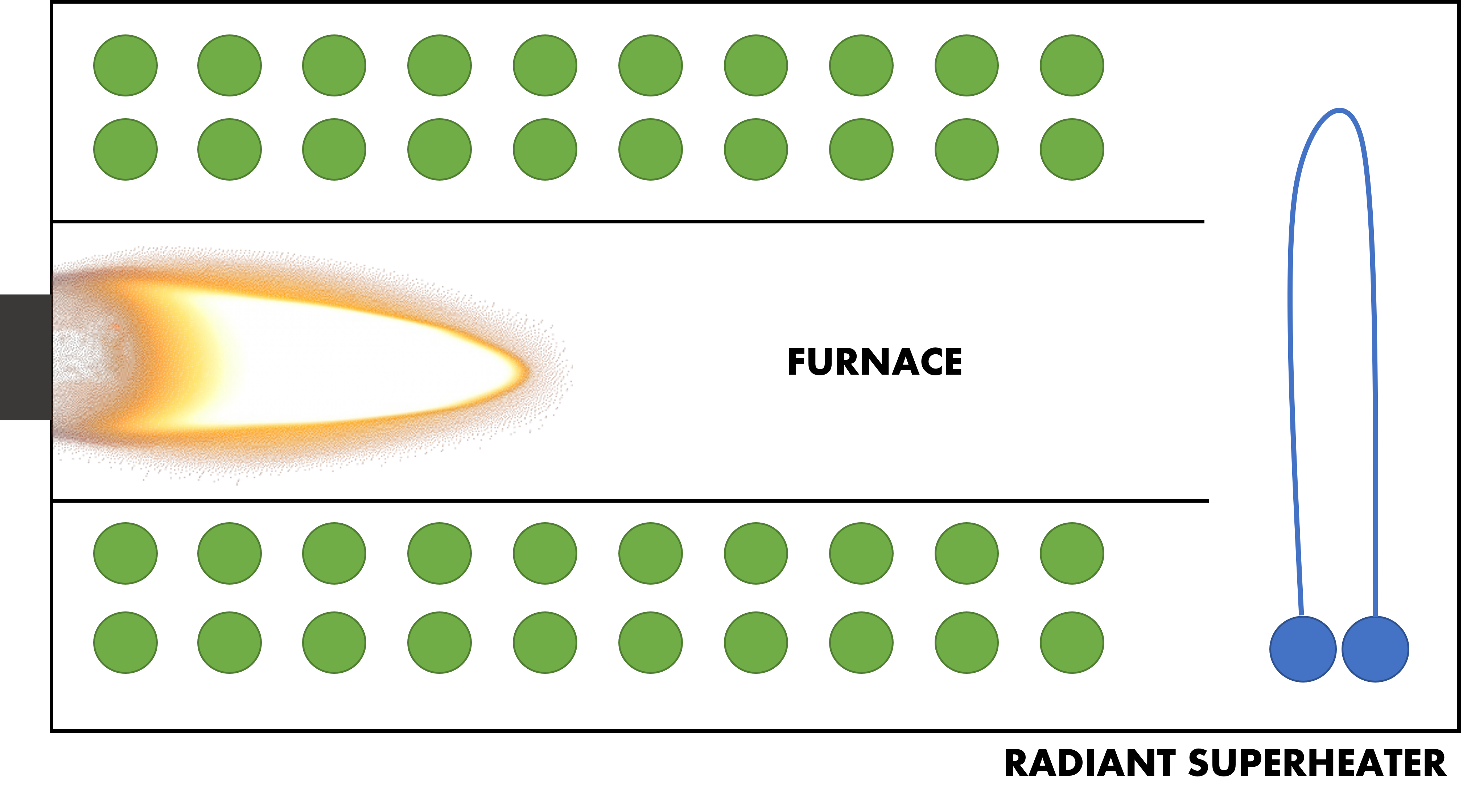
On O-type and A-type boilers, the extra tube bank is added at the end of the furnace. This is called the radiant design. The benefit of this design is that the performance is much better as compared to the convective style throughout the load range. However, since the heat transferred is primarily radiant heat from the burner, the superheater typically doesn’t last as long and requires more maintenance.
In today’s market, D-Type boilers are the most common. The superheat performance issues can be compensated by designing the steam for a higher temperature and then using an attemperator to control steam temperature more closely over the boiler load range. In the rental boiler industry, O-type boilers are the most common because the weight is more evenly distributed making it ideal for trailer-mounting and road transportation. Stay tuned for our next blog where we will touch on a fourth, less commonly known watertube design; the Ds-type. Ds style boilers are patented and manufactured by Superior Boiler.
As a rental boiler supplier, manufacturer’s representative and stocking distributor, Nationwide Boiler has not only sold but actually operated and maintained package watertube boilers for over 50 years. Give us a call today to learn more about what type of boiler is best for your unique application.


