At Nationwide Boiler, we are known for our relationship with B&W as a partner and stocking distributor. The FM-120-124 B&W D-Type Package Watertube Boiler, also known as our “World Boiler”, is always in stock and has been sold to six of the seven continents in the world. In recent years, we have ramped up our stock boiler program to also include new Superior firetube boilers in a variety of configurations.
To start off, we added two specialized, factory integrated packages. These 47.5 hp and 119 hp skid-mounted package boilers are pre-piped and wired and include a duplex feedwater system and blowdown separator with after-cooler. The 47.5 hp boilers are pre-certified for use in the most stringent California air districts, while the 119 hp packages are PEER compatible for both the SCAQMD and SJVAPCD jurisdictions. Our 475 hp, 150 psi design Superior skid-mounted firetube boiler, equipped with a Webster 7ppm NOx burner, is also ideal for customers in the most stringent areas of California. All three of these systems are currently available from our shop in Fremont, CA.
To round out our stock inventory of pacakge firetube boilers, we now have the following brand new Superior boilers available for quick ship and immediate needs:
- 200 hp, 200 psig Skid-Mounted Firetube Boiler
- 300 hp, 250 psig Skid-Mounted Firetube Boiler
- 350 hp, 250 psig Skid-Mounted Firetube Boiler
- 700 hp, 250 psig Skid-Mounted Firetube Boiler
- 800 hp, 250 psig Skid-Mounted Firetube Boiler
These stock boilers are pre-built with the burner left purposely un-mounted to allow for greater flexibility in matching the unique fuel, emissions, and combustion needs of each customer. The burner can be quickly mounted prior to delivery or installed at the site, based on customer preference. The boilers are designed for indoor and outdoor applications, with most currently being stored at the manufacturing facility in Hutchison, KS. All units are now available for immediate shipment upon customer request.
We also have our very first, zero emissions electric boiler now available for rent or for sale. This boiler, built to provide 50 hp steam at a design pressure of 150 psig, is another one of our factory integrated units, with feedwater system and blowdown separator pre-piped and wired as a skid-package.
In addition to the new boilers that we purchase specifically for our stocking program, our fleet of rental boilers and auxiliary equipment range in size and in age. We are always open to providing a solution from our rental fleet as well, if the opportunity arises. Be sure to check out or complete inventory of boilers available for sale to find a unit that fits your unique needs.
Please give us a call at 800-227-1966 if you have an immediate boiler need that can be fulfilled from our stock of brand new boilers, reconditioned boilers, or equipment from our rental fleet.
And check out our latest Steamlines newsletter, to find this article as well as other recent project highlights, equipment spotlights, and company updates.



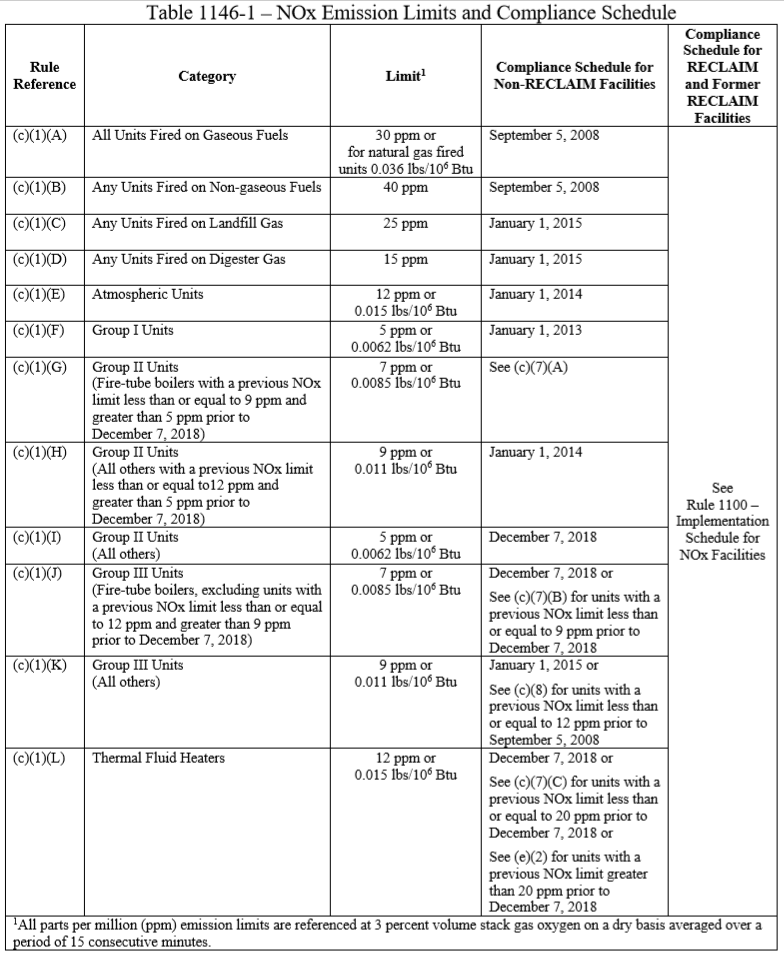 Within the RECLAIM standards, Rule 1146 outlines specific guidelines for boilers, steam generators, and process heaters that have a heat input of 5 mmBtu/hr or greater, that are utilized in all industrial, institutional, and commercial operations. This rule has changed several times, and at the end of 2018, another revision to the rule was adopted. All Group 1 units (>/= 75MMBTu/hr) as well as Group II units (20 - 75 MMBTu/hr) with an existing permit limit greater than 2 ppm must comply with a 5 ppm NOx limit. In addition, facilities that qualify must be in compliance by 2022 – 2023. The table below outlines all equipment and current limits based on category and heat input.
Within the RECLAIM standards, Rule 1146 outlines specific guidelines for boilers, steam generators, and process heaters that have a heat input of 5 mmBtu/hr or greater, that are utilized in all industrial, institutional, and commercial operations. This rule has changed several times, and at the end of 2018, another revision to the rule was adopted. All Group 1 units (>/= 75MMBTu/hr) as well as Group II units (20 - 75 MMBTu/hr) with an existing permit limit greater than 2 ppm must comply with a 5 ppm NOx limit. In addition, facilities that qualify must be in compliance by 2022 – 2023. The table below outlines all equipment and current limits based on category and heat input.